In a heat wave, your cannabis garden may face the threat of plant heat stress symptoms, a critical issue that can hinder plant health, yield, and overall success. Recognizing and understanding these symptoms—ranging from wilting and leaf scorching to more complex issues like humidity imbalances and ozone damage—are essential in safeguarding your plants against the harsh effects of extreme temperatures.
Heat stress in plants, particularly cannabis, demands prompt attention, as it can dramatically affect plant stress tolerance, potentially leading to plants dying from heat without effective intervention. The significance of addressing heat stress symptoms extends beyond immediate plant health, impacting the long-term sustainability and productivity of cannabis gardens.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide, starting with a deep dive into understanding heat stress in cannabis gardens, including identifying plant heat stress symptoms and the science behind plant stress and heat tolerance. Subsequently, it discusses strategies for preventing heat stress, focusing on measures such as optimizing relative humidity and using mulch to regulate soil temperature.
Understanding Heat Stress in Cannabis Gardens
Definition and Causes of Heat Stress
Cannabis heat stress occurs when the environmental conditions exceed the temperature thresholds that the plant’s biochemistry can tolerate. This stress is not merely about the plant experiencing warmth but a significant physiological response when the temperatures rise beyond its comfort zone.
Several factors contribute to heat stress, including excessive light, which increases the plant’s internal temperature, and poor ventilation in grow rooms, which fails to remove heat efficiently. Additionally, equipment failures such as malfunctioning temperature sensors or extraction fans can exacerbate the situation.
Effects of Heat Stress on Cannabis Plants
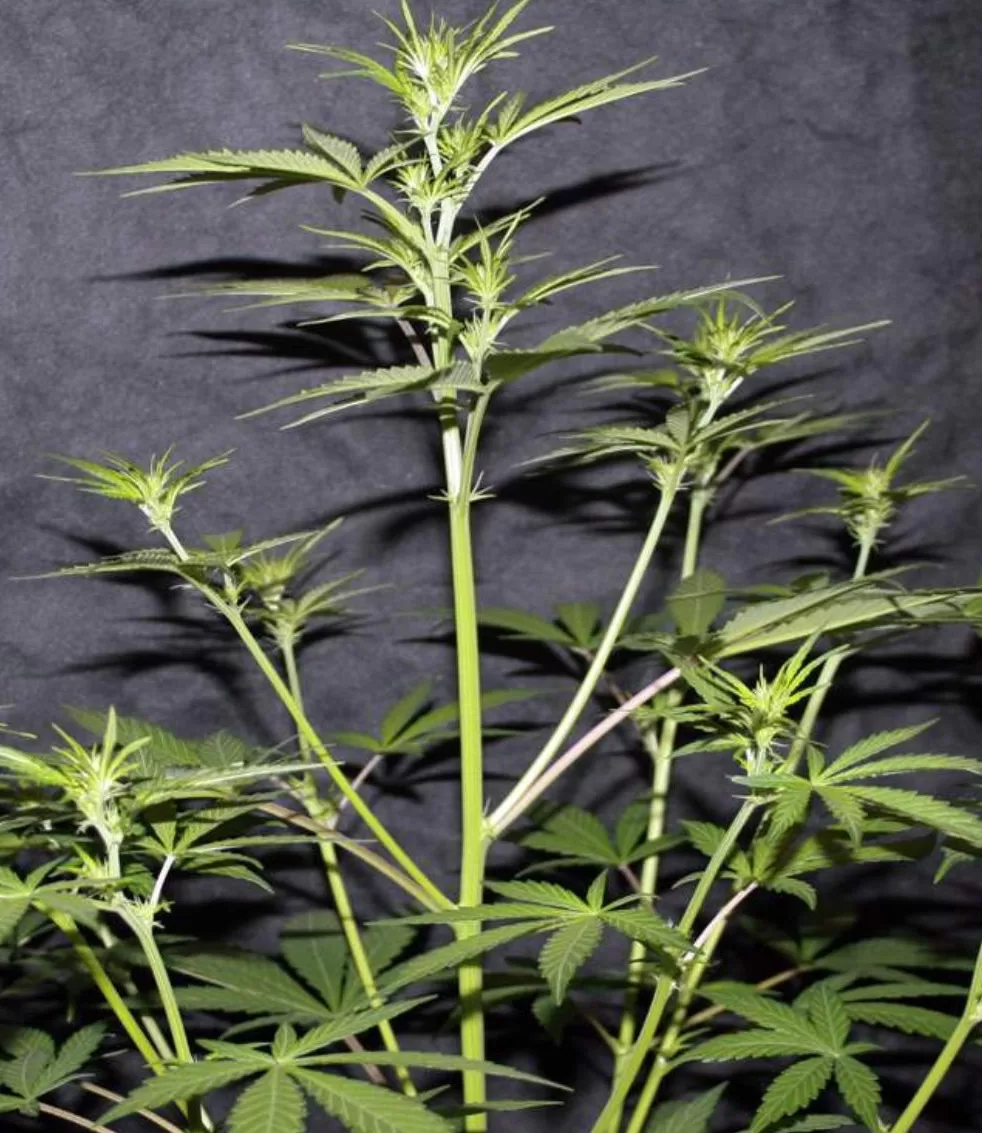
The impact of heat stress on cannabis plants is multifaceted. Initially, high temperatures can cause fundamental disruptions in cellular functions, making essential processes like photosynthesis and respiration brutal. This can lead to symptoms such as leaf curling, where the edges curl upwards to reduce exposure to intense light and heat.
In severe cases, the leaves may become dry and crispy, and the plant may exhibit stunted growth. Chronic heat stress can also affect the plant’s reproductive phase, reducing the quality and potency of buds by decreasing THC and terpene production.
Furthermore, heat stress can lead to nutrient problems, either by causing nutrient burn or reducing the plant’s ability to uptake nutrients due to decreased water absorption.
Preventing Plant Heat Stress Symptoms in Your Cannabis Garden
Temperature and Humidity Control
To plant heat stress symptoms in cannabis gardens, maintaining an optimal temperature range between 70°F and 85°F (21°C and 29°C) is crucial. Effective temperature control can be achieved through air conditioning, enhanced ventilation, and strategic shading.
Additionally, humidity plays a pivotal role in plant health, especially in enclosed environments like greenhouses, where proper ventilation and humidification techniques are necessary to maintain humidity levels conducive to seedling development and prevent excessive moisture loss 11.
Proper Watering Techniques
Watering practices significantly influence the health of cannabis plants. It is essential to water deeply yet infrequently to promote robust root development and minimize evaporation. Ensuring the plants receive adequate moisture without overwatered prevents stress and maintains efficient nutrient uptake.
Adjusting watering schedules according to the heat levels—preferably during more excellent parts of the day—can also prevent water stress and enhance absorption.
Shading and Light Management
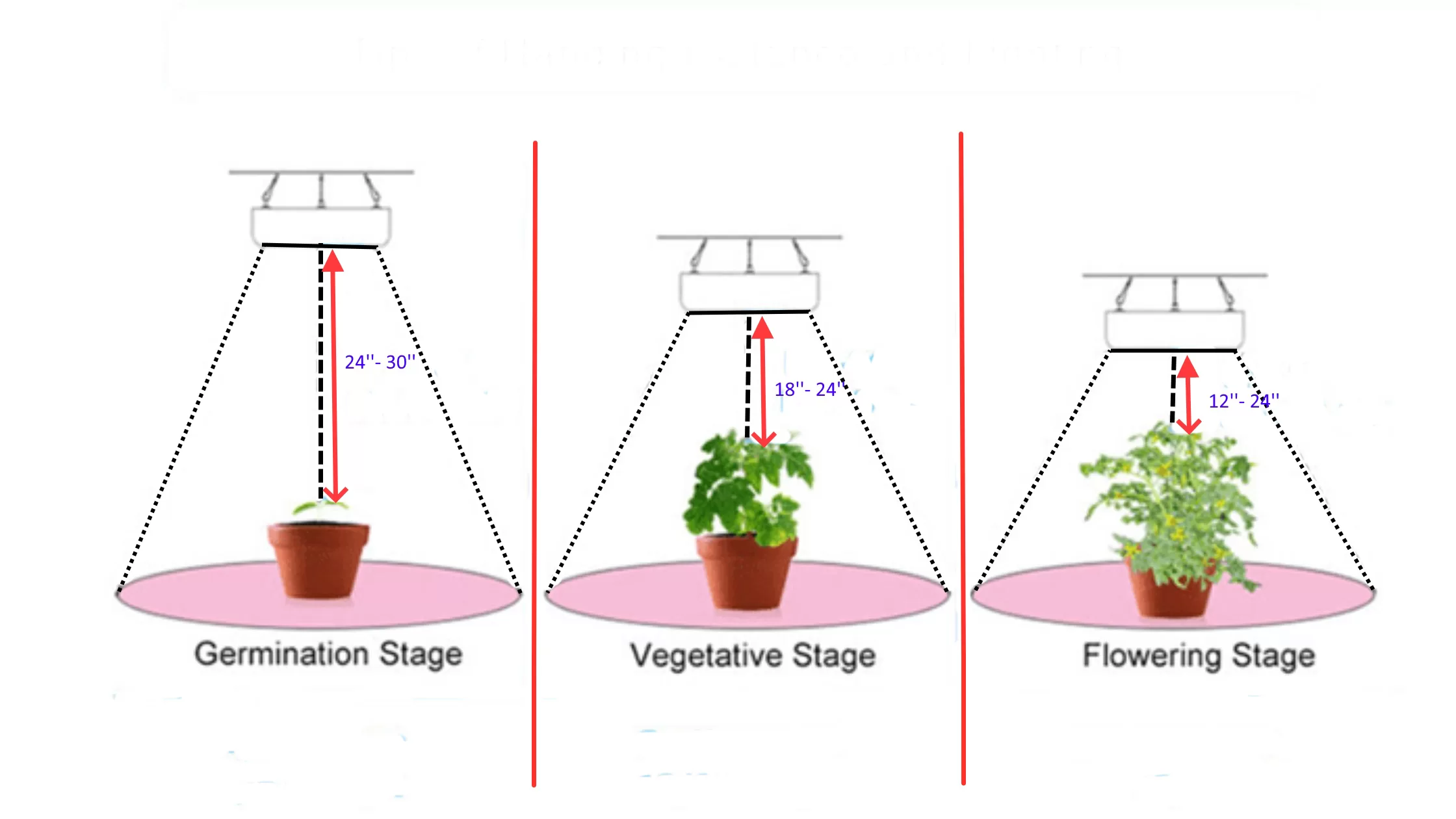
Shading solutions can protect cannabis plants from intense sunlight and artificial light exposure, crucial in preventing overheating and light stress. Utilizing shade cloths, adjusting grow light setups, and employing natural shade from surrounding vegetation or structures can significantly reduce heat stress. Managing the distance between grow lights and plants is essential for indoor environments to avoid heat buildup and potential plant damage.
Managing Indoor Cannabis Heat Stress
Optimizing Ventilation and Air Circulation
Adequate ventilation is crucial in managing heat stress in indoor cannabis gardens. Proper air circulation helps regulate temperature, preventing hot spots and creating a more uniform growing environment. Oscillating fans inside the grow space promote gentle air movement, mimicking natural breezes, strengthening plant stems, preventing heat stress, and enhancing nutrient uptake.
Additionally, ventilation systems such as exhaust fans and ducting are essential as they remove stale air, excess heat, and humidity, facilitating the exchange of indoor and outdoor air. Aim for optimal airflow of ventilation inlets horizontally at the canopy level and buds without aiming directly at the plants.
Using Grow Lights Efficiently
LED grow lights are recommended for their reduced heat output, which minimizes heat stress on cannabis plants. They can be placed closer to the canopy without the risk of burning the plants, allowing for better light penetration and utilization.
However, even LED lights generate heat, and it’s essential to ensure the grow room or tent is adequately ventilated to keep the temperature within the optimal range for cannabis growth. The power and intensity of LED lights should be chosen and adjusted carefully to match the growing area and plant growth stage.
Air Conditioning and Supplemental Tools
In addition to optimizing ventilation and using grow lights efficiently, employing air conditioning and dehumidification systems can further assist in managing indoor heat stress.
HVAC systems should be sized and selected to maintain target space temperature and relative humidity while providing continuous airflow for general circulation.
Supplemental dehumidifiers or a packaged air-handling unit with DX cooling can generate a low dewpoint required for dehumidification, making supplemental dehumidifiers unnecessary.
For more extensive facilities, a chilled water system with heating hot water or other means of reheating/post-heating might be employed to ensure the success of the growing plants.

Managing Outdoor Cannabis Heat Stress
Choosing Heat-Resistant Strains
Selecting the right cannabis strains is crucial for managing heat stress in outdoor environments. Some strains, particularly those originating from hot climates like Sativa, Haze, African, and Hawaiian, are more heat-resistant and can thrive under intense sunlight and high temperatures.
For instance, strains like Durban Poison and Super Lemon Haze are known for their ability to handle the heat, making them suitable choices for growers in warmer climates.
Additionally, incorporating genetics such as White Widow, which combines heat-resistant traits, can further enhance the robustness of your garden against heat stress.
Relocating and Shading Plants
To prevent plant heat stress symptoms, it is advisable to gradually acclimate plants to outdoor conditions. Start by placing them in a shaded area and slowly increase their exposure to direct sunlight. Utilizing shade cloths, especially during the peak sun hours from 11 AM to 4 PM, can protect plants from excessive heat and light.
Additionally, consider the strategic placement of plants to take advantage of natural shade and protect them from environmental stressors like strong winds and heavy rains.
Timing and Techniques for Watering
Watering techniques play a pivotal role in managing heat stress. It is essential to check the soil’s moisture level and water the plants accordingly, avoiding under and over-watering.
Watering should be done early in the morning to allow plants to absorb moisture before the heat intensifies.
For outdoor cannabis plants, especially in hot climates, increasing the watering frequency while ensuring proper drainage can prevent stress and support healthy growth.
Employing a drip irrigation system can also maintain consistent soil moisture and reduce temperature fluctuations.
Additional Tips and Best Practices
Monitoring and Adjusting Conditions
- Regularly monitor plants for early signs of heat stress, such as wilting, leaf curling, discoloration, and reduced growth rates.
- Adjust watering schedules and provide extra shade to mitigate heat stress if necessary.
- Ensure proper air circulation to dissipate heat and maintain an optimal microclimate around cannabis plants.
Using Supplements and Soil Enhancements
- Apply supplements like yucca, kelp, fulvic acid, and silicon to enhance plants’ natural defense mechanisms against heat stress.
- Use seaweed or kelp extracts loaded with minerals and nutrients, making plants more resistant to high temperatures.
- Incorporate mycorrhizal fungi, which form symbiotic relationships with cannabis plants, enhancing water absorption and nutrient uptake, thus mitigating drought and heat stress.
Long-term Strategies for Heat Stress Prevention
- Consider genetic tweaks to cultivate strains more adapted to regional climate conditions.
- Employ shade cloths and mulching to regulate soil temperature and reduce direct sunlight impact.
- Plan planting schedules to avoid peak heat periods, establishing young plants before high-temperature seasons.
These strategies, when combined, provide a robust framework for managing and preventing heat stress in cannabis gardens, ensuring healthy plant growth and optimal yields.
Conclusion
Heat stress can be a formidable challenge for gardeners, but with this comprehensive guide, you’ll be well-equipped to prevent and manage it. You can keep your plants cool, healthy, and thriving by understanding the causes of heat stress and implementing effective strategies like monitoring and controlling temperature, improving air circulation, providing shade, and adjusting watering and feeding schedules.
So, beat the heat and watch your garden flourish, even in the face of rising temperatures!
Join Our Community: Connect with Fellow Cannabis Gardeners for Tips and Support
FAQs
Can Plants Bounce Back from Heat Stress?
Yes, plants can recover from heat stress, but the recovery period can vary significantly. Depending on the extent of the damage, it might take a few days to several months for a plant to fully recuperate from heat stress.
How Can You Tell if a Cannabis Plant is Overheated?
An overheated cannabis plant will exhibit several distinct signs. The tips of the leaves may appear burnt and start to curl, and as the condition worsens, browning may spread downward through the plant. The canopy leaves might turn bleached and yellow, and the leaves will likely curl up instead of lying flat.
Is it Possible for Cannabis to Grow at 100 Degrees Fahrenheit?
Cannabis plants thrive best in temperatures between 70 and 80 degrees Fahrenheit (21 and 27 degrees Celsius). However, they can also grow well at temperatures up to 95 degrees Fahrenheit (35 degrees Celsius), especially in environments well-lit and rich in CO2. To help manage heat, growers often elevate planters and pots on tables to minimize the cooling effects of the floor on the root systems.
What Does Temperature Stress Mean for Cannabis Plants?
Temperature stress in cannabis plants refers to the adverse effects that occur when the plants are exposed to temperatures outside their ideal range. Exposure to high temperatures can induce heat stress, leading to symptoms such as wilting, leaf curling, a decline in photosynthesis, and a reduction in overall yield.